

When the membrane is at rest, K + ions accumulate inside the cell due to a net movement with the concentration gradient. The difference in the number of positively charged potassium ions (K +) inside and outside the cell dominates the resting membrane potential ( Figure 16.10). Because ions cannot simply cross the membrane at will, there are different concentrations of several ions inside and outside the cell, as shown in Table 16.1. If the membrane were equally permeable to all ions, each type of ion would flow across the membrane and the system would reach equilibrium. This voltage is called the resting membrane potential it is caused by differences in the concentrations of ions inside and outside the cell. After activation, they become inactivated for a brief period and will no longer open in response to a signal.Ī neuron at rest is negatively charged: the inside of a cell is approximately 70 millivolts more negative than the outside (−70 mV, note that this number varies by neuron type and by species). Voltage-gated ion channels open in response to changes in membrane voltage. The difference in total charge between the inside and outside of the cell is called the membrane potential. Voltage-gated ion channels regulate the relative concentrations of different ions inside and outside the cell. Ion channels that change their structure in response to voltage changes are called voltage-gated ion channels.
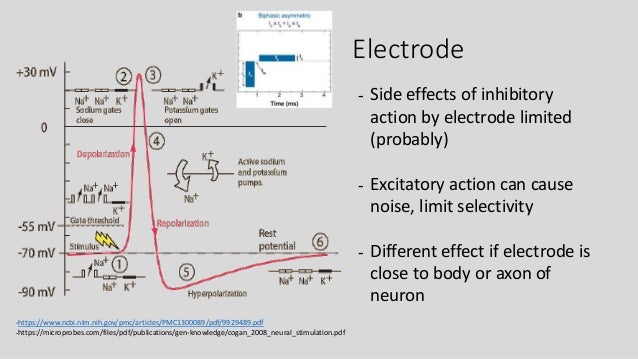
These ion channels are sensitive to the environment and can change their shape accordingly. Some ion channels need to be activated in order to open and allow ions to pass into or out of the cell. Ion channels have different configurations: open, closed, and inactive, as illustrated in Figure 16.9. To enter or exit the neuron, ions must pass through special proteins called ion channels that span the membrane. The lipid bilayer membrane that surrounds a neuron is impermeable to charged molecules or ions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
